What is CTX?
Cerebrotendinous xanthomatosis (CTX) is a rare genetic disorder affecting the proper breakdown of cholesterol.
CTX is caused by defects in the CYP27A1 gene leading to a deficiency of a crucial enzyme thus interrupting cholesterol breakdown into primary bile acids, chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and cholic acid (CA). This results in a deficiency of these primary bile acids, especially of CDCA as CA is also produced through an alternate mechanism not requiring the enzyme that is affected. The deficiency of primary bile acids disrupts how cholesterol is normally removed and leads to an increase in abnormal toxic compounds and an abnormal accumulation of lipids in the body.
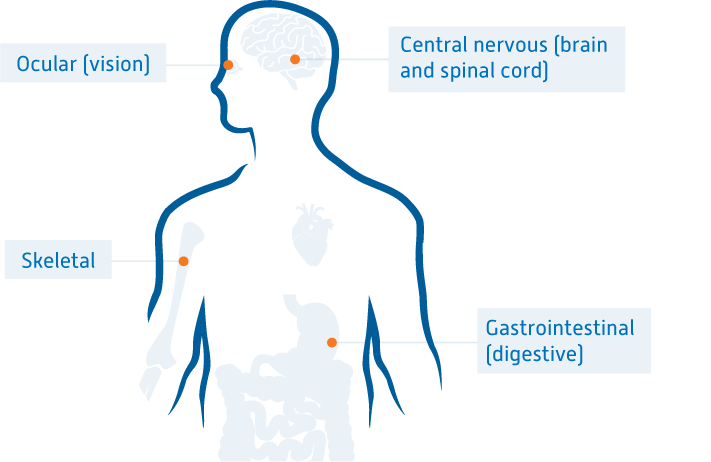
The disease is characterized by the abnormal storage of these lipids in various areas of the body, causing potentially devastating, progressive symptoms in the eyes, tendons, and central nervous system. CTX affects patients’ long-term health and quality of life.1,2